Abstract
Mini Review
ABC and MFS Transporters: A reason for Antifungal drug resistance
Neelabh* and Karuna Singh
Published: 05 January, 2018 | Volume 2 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-007
Fungi cause a variety of diseases and are difficult to treat owing to their eukaryotic nature resulting in dearth of antifungal targets at hand. This problem is further elevated many folds due to the resistance mechanisms of fungi through which they circumvent the antifungal drugs administered for therapeutic purposes. Fungi have a variety of strategies for obtaining these resistances, amongst them pivotal role is played by the ABC and MFS transporters. This article encompasses the important genes and their respective roles of both the classes of the transporters in different species of fungi.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.abb.1001009 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Fungi; Resistance; Transporters; ABC; MFS
References
- Pianalto KM, Alspaugh JA. New Horizons in antifungal therapy.J Fungi.2016; 4: 26. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Ay5dYZ
- Brown GD, Denning DW, Gow NA, Levitz SM, Netea MG, et al. Hidden killers: human fungal infections.Sci Transl Med. 2012; 165: 165. Ref.: https://goo.gl/33Aymv
- Chu DT, Plattner JJ, Katz L. New directions in antibacterial research.J Med Chem. 1996;39: 3853-3874. Ref.: https://goo.gl/VCmMK4
- Kontoyiannis DP, Lewis RE. Antifungal drug resistance of pathogenic fungi. Lancet. 2002; 359: 1135-1144. Ref.: https://goo.gl/439pW7b
- Sanglard D, Coste A, Ferrari S. Antifungal drug resistance mechanisms in fungal pathogens from the perspective of transcriptional gene regulation.FEMS Yeast Res. 2009;9: 1029-1050. Ref.: https://goo.gl/zEHzqX
- Cannon RD, Lamping E, Holmes AR, Niimi K, Baret PV, et al. Efflux-mediated antifungal drug resistance.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009; 22: 291-321. Ref.: https://goo.gl/FFooGK
- Bauer BE, Wolfger H, Kuchler K. Inventory and function of yeast ABC proteins: about sex, stress, pleiotropic drug and heavy metal resistance.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999; 1461: 217-236. Ref.: https://goo.gl/go9UVs
- Decottignies A, Goffeau A. Complete inventory of the yeast ABC proteins.Nat Genet. 1997; 15: 137-145. Ref.: https://goo.gl/xcUV5X
- Sipos G, Kuchler K. Fungal ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in drug resistance & detoxification.Curr Drug Targets. 2006; 7: 471-481. Ref.: https://goo.gl/4A6ijR
- Balzi E, Wang M, Leterme S, Van Dyck L, Goffeau A. PDR5, a novel yeast multidrug resistance conferring transporter controlled by the transcription regulator PDR1.J Biol Chem. 1994; 269: 2206-2214. Ref.: https://goo.gl/U3bTgk
- Bissinger PH, Kuchler K. Molecular cloning and expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae STS1 gene product. A yeast ABC transporter conferring mycotoxin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1994; 269: 4180-4186. Ref.: https://goo.gl/iz8FPk
- Hirata D, Yano K, Miyahara K, Miyakawa T. Saccharomyces cerevisiae YDR1, which encodes a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) superfamily, is required for multidrug resistance.Curr Genet. 1994;26: 285-294. Ref.: https://goo.gl/wHgpxt
- Sanglard D, Kuchler K, Ischer F, Pagani JL, Monod M, et al. Mechanisms of resistance to azole antifungal agents in Candida albicans isolates from AIDS patients involve specific multidrug transporters.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995; 39: 2378-2386. Ref.: https://goo.gl/NEkJb6
- Sanglard D, Ischer F, Monod M, Bille J. Susceptibilities of Candida albicans multidrug transporter mutants to various antifungal agents and other metabolic inhibitors.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996; 40: 2300-2305. Ref.: https://goo.gl/mNijQx
- Sanglard D, Ischer F, Monod M, Bille J. Cloning of Candida albicans genes conferring resistance to azole antifungal agents: characterization of CDR2, a new multidrug ABC transporter gene.Microbiology. 1997: 143: 405-416. Ref.: https://goo.gl/LWV1ux
- White TC. Increased mRNA levels of ERG16, CDR, and MDR1 correlate with increases in azole resistance in Candida albicans isolates from a patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1997; 41: 1482-1487. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qJpXFb
- White TC, Holleman S, Dy F, Mirels LF, Stevens DA. Resistance mechanisms in clinical isolates of Candida albicans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002; 46: 1704-1713. Ref.: https://goo.gl/4YHXtY
- Ramage G, Bachmann S, Patterson TF, Wickes BL, López-Ribot JL. Investigation of multidrug efflux pumps in relation to fluconazole resistance in Candida albicans biofilms.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002; 49: 973-980. Ref.: https://goo.gl/FBHFNd
- Balan I, Alarco AM, Raymond M. The Candida albicans CDR3 gene codes for an opaque-phase ABC transporter. Journal of bacteriology. 1997: 179. 7210-7218. Ref.: https://goo.gl/gfpPgY
- Franz R, Michel S, Morschhäuser J. A fourth gene from the Candida albicans CDR family of ABC transporters.Gene. 1998; 220: 91-98. Ref.: https://goo.gl/oDtXD3
- Cui Z, Hirata D, Miyakawa T. Functional analysis of the promoter of the yeast SNQ2 gene encoding a multidrug resistance transporter that confers the resistance to 4-nitroquinoline N-oxide. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1999; 1: 162-167. Ref.: https://goo.gl/GMGyVG
- Oliveira K, Haase G, Kurtzman C, Jo J, Stender H. Differentiation of Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis by fluorescent in situ hybridization with peptide nucleic acid probes. J Clin Microbiol. 2001; 11: 4138-4141. Ref.: https://goo.gl/wSd1Tk
- Borst A, Raimer MT, Warnock DW, Morrison CJ, Arthington-Skaggs BA. Rapid acquisition of stable azole resistance by Candida glabrata isolates obtained before the clinical introduction of fluconazole.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2005; 2: 783-787. Ref.: https://goo.gl/J9CgcQ
- Sanguinetti M, Posteraro B, Fiori B, Ranno S, Torelli R, et al. Mechanisms of azole resistance in clinical isolates of Candida glabrata collected during a hospital survey of antifungal resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2005; 2: 668-679. Ref.: https://goo.gl/yHRQdL
- Miyazaki H, Miyazaki Y, Geber A, Parkinson T, Hitchcock C, et al. Fluconazole resistance associated with drug efflux and increased transcription of a drug transporter gene, PDH1, in Candida glabrata.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.1998; 7: 1695-1701. Ref.: https://goo.gl/cWM5wU
- Sanglard D, Ischer F, Calabrese D, Majcherczyk PA, Bille J. The ATP binding cassette transporter GeneCgCDR1 from Candida glabrata is involved in the resistance of clinical isolates to azole antifungal agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999; 11: 2753-2765. Ref.: https://goo.gl/bti7d3
- Nakayama H, Izuta M, Nakayama N, Arisawa M, Aoki Y. Depletion of the squalene synthase (ERG9) gene does not impair growth of Candida glabrata in mice.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2000; 9: 2411-2418. Ref.: https://goo.gl/wJERXi
- Fukuoka T, Johnston DA, Winslow CA, de Groot MJ, Burt C, et al. Genetic basis for differential activities of fluconazole and voriconazole against Candida krusei. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003; 4: 1213-1219. Ref.: https://goo.gl/6DGpJh
- Orozco AS, Higginbotham LM, Hitchcock CA, Parkinson T, Falconer D, et al. Mechanism of Fluconazole Resistance in Candida krusei. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998; 10: 2645-2649. Ref.: https://goo.gl/aNv2HZ
- Venkateswarlu K, Denning DW, Kelly SL. Inhibition and interaction of cytochrome P450 of Candida krusei with azole antifungal drugs.J Med Vet Mycol.1997; 1: 19-25. Ref.: https://goo.gl/n36Rwe
- Moran GP, Sanglard D, Donnelly SM, Shanley DB, Sullivan DJ, et al. Identification and expression of multidrug transporters responsible for fluconazole resistance in Candida dubliniensis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.1998; 7: 1819-1830. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Mf42BU
- Barchiesi F, Calabrese D, Sanglard D, Di Francesco LF, Caselli F, et al. Experimental induction of fluconazole resistance in Candida tropicalis ATCC 750.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2000; 6: 1578-1584. Ref.: https://goo.gl/dpRzv1
- Katiyar SK, Edlind TD. Identification and expression of multidrug resistancerelated ABC transporter genes in Candida krusei. Med Mycol. 2001; 1: 109-116. Ref.: https://goo.gl/fsrs5z
- Slaven JW, Anderson MJ, Sanglard D, Dixon GK, Bille J, et al. Increased expression of a novel Aspergillus fumigatus ABC transporter gene, atrF, in the presence of itraconazole in an itraconazole resistant clinical isolate.Fungal Genet Biol.2002; 3: 199-206. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Lt1m6A
- Tekaia F, Latgé JP. Aspergillus fumigatus: saprophyte or pathogen?. Current opinion in Microbiology.2005; 4: 385-392. Ref.: https://goo.gl/rrDhR1
- Hu W, Sillaots S, Lemieux S, Davison J, Kauffman S, et al. Essential gene identification and drug target prioritization in Aspergillus fumigatus.PLoS Pathog.2007; 3: 24. Ref.: https://goo.gl/wk5Asm
- Andrade AC, Del Sorbo G, Van Nistelrooy JG, De Waard MA. The ABC transporter AtrB from Aspergillus nidulans mediates resistance to all major classes of fungicides and some natural toxic compounds. Microbiology.2000; 8: 1987-1997. Ref.: https://goo.gl/9KKDbR
- Andrade AC, Van Nistelrooy JGM, Peery RB, Skatrud PL, De Waard MA. The role of ABC transporters from Aspergillus nidulans in protection against cytotoxic agents and in antibiotic production.Mol Gen Genet.2000; 6: 966-977. Ref.: https://goo.gl/SiYTHx
- Angermayr K, Parson W, Stöffler G, Haas H. Expression of atrC-encoding a novel member of the ATP binding cassette transporter family in Aspergillus nidulans-is sensitive to cycloheximide.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999; 2: 304-310. Ref.: https://goo.gl/omCCgD
- Del Sorbo G, Andrade AC, Van Nistelrooy JGM, Van Kan JAL, Balzi E, et al. Multidrug resistance in Aspergillus nidulans involves novel ATP-binding cassette transporters. Mol Gen Genet. 1997; 4: 417-426. Ref.: https://goo.gl/L8y1jg
- Posteraro B, Sanguinetti M, Sanglard D, La Sorda M, Boccia S, et al. Identification and characterization of a Cryptococcus neoformans ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter‐encoding gene, CnAFR1, involved in the resistance to fluconazole.Mol Microbiol.2003; 2: 357-371. Ref.: https://goo.gl/XtZ598
- Sanguinetti M, Posteraro B, La Sorda M, Torelli R, Fiori B, et al. Role of AFR1, an ABC transporter-encoding gene, in the in vivo response to fluconazole and virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans.Infect Immun.2006; 2: 1352-1359. Ref.: https://goo.gl/VJYGGv
- Thornewell SJ, Peery RB, Skatrud PL. Cloning and characterization of CneMDR1: a Cryptococcus neoformans gene encoding a protein related to multidrug resistance proteins.Gene.1997; 1: 21-29. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qsedCC
- Venkateswarlu K, Taylor M, Manning NJ, Rinaldi MG, Kelly SL. Fluconazole tolerance in clinical isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.1997; 4: 748-751. Ref.: https://goo.gl/PnUwMR
- Gbelska Y, Krijger JJ, Breunig KD. Evolution of gene families: the multidrug resistance transporter genes in five related yeast species.FEMS Yeast Res.2006; 3: 345-355. Ref.: https://goo.gl/sbwmT6
- Lamping E, Monk BC, Niimi K, Holmes AR, Tsao S, et al. Characterization of three classes of membrane proteins involved in fungal azole resistance by functional hyperexpression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eukaryot Cell. 2007; 7: 1150-1165. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Ts2gMZ
- Pasrija R, Banerjee D, Prasad R. Structure and function analysis of CaMdr1p, a major facilitator superfamily antifungal efflux transporter protein of Candida albicans: identification of amino acid residues critical for drug/H+ transport.Eukaryot Cell. 2007; 3: 443-453. Ref.: https://goo.gl/TfvHHj
- Calabrese D, Bille J, Sanglard D. A novel multidrug efflux transporter gene of the major facilitator superfamily from Candida albicans (FLU1) conferring resistance to fluconazole.Microbiology.2000; 11: 2743-2754. Ref.: https://goo.gl/7rQfQY
Figures:
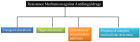
Figure 1
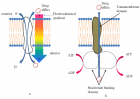
Figure 2
Similar Articles
-
Overview of Interferon: Characteristics, signaling and anti-cancer effectKangjian Zhang*,Huaiyuan Wang,Haijun Hu. Overview of Interferon: Characteristics, signaling and anti-cancer effect. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hjb.1001001; 1: 001-016
-
ABC and MFS Transporters: A reason for Antifungal drug resistanceNeelabh*,Karuna Singh. ABC and MFS Transporters: A reason for Antifungal drug resistance. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.abb.1001009; 2: 001-007
-
Antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from urine in hospital patients and outpatientsZeljko Cvetnić*,Maja Ostojic,Mahir Hubana,Marija Cvetnić,Miroslav Benić. Antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from urine in hospital patients and outpatients. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.abb.1001021; 5: 001-007
-
Detection of extended-spectrum betalactamase and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in TunisiaRahma Trabelsi*,Mariem Yengui,Amel Mhaya,Ahmed Rebai,Corinne Arpin,Radhouane Gdoura. Detection of extended-spectrum betalactamase and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Tunisia. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.abb.1001034; 7: 001-011
-
Production of L-Asparaginase by Yemeni Filamentous FungiMaysoon A Al Zubairy*, Faten H Thamer, Habib Thabet, Khawlah Shrf Aldeen. Production of L-Asparaginase by Yemeni Filamentous Fungi. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.abb.1001036; 7: 018-023
-
Effect of Methyl Jasmonate on the Expression of Transcription Factors in Wild Jujube Seedlings under Salt StressJianing Chen, Guangping Wang, Hanyun Liang, Yan Zhao, Xin Gao, Xiankuan Li*, Jian Zhang*. Effect of Methyl Jasmonate on the Expression of Transcription Factors in Wild Jujube Seedlings under Salt Stress. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.abb.1001038; 8: 003-008
-
Antibacterial Resistance and Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL) Phenotypes in Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Fecal Samples of Humans and Animals in Selected Local Government Areas of Nasarawa State, NigeriaRICHARD R*, EZEJIOFOR T.I.N, NSOFOR C.A, MANINGI N.E. Antibacterial Resistance and Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL) Phenotypes in Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Fecal Samples of Humans and Animals in Selected Local Government Areas of Nasarawa State, Nigeria. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.abb.1001041; 8: 027-033
Recently Viewed
-
Comparative Studies of Diclofenac Sodium (NSAID) Adsorption on Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Bran and Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) Shell Powder using Vertical and Sequential Bed ColumnNeha Dhiman*. Comparative Studies of Diclofenac Sodium (NSAID) Adsorption on Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Bran and Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) Shell Powder using Vertical and Sequential Bed Column. Ann Adv Chem. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.aac.1001052; 8: 021-029
-
Pulsed Shortwave Diathermy and Joint Mobilizations Restore a Twice Fractured Elbow with Metal Implants to Full Range of MotionDavid O. Draper*,Emily Veazey. Pulsed Shortwave Diathermy and Joint Mobilizations Restore a Twice Fractured Elbow with Metal Implants to Full Range of Motion. J Nov Physiother Rehabil. 2017: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001003; 1: 020-026
-
Assessment of Perceptions of Nursing Undergraduates towards Mental Health PracticesAlya Algamdii*. Assessment of Perceptions of Nursing Undergraduates towards Mental Health Practices. Clin J Nurs Care Pract. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001059; 9: 007-011
-
New insights of liquid biopsy in ovarian cancerPanagiotis Antoniadis*,Florentina Alina Gheorghe,Madalina Ana Maria Nitu,Cezara Gabriela Nitu,Diana Roxana Constantinescu,Florentina Duica. New insights of liquid biopsy in ovarian cancer. J Genet Med Gene Ther. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.jgmgt.1001007; 5: 001-011
-
Clinical Severity of Sickle Cell Anaemia in Children in the Gambia: A Cross-Sectional StudyLamin Makalo,Samuel A Adegoke,Stephen J Allen,Bankole P Kuti,Kalipha Kassama,Sheikh Joof,Aboulie Camara,Mamadou Lamin Kijera,Egbuna O Obidike. Clinical Severity of Sickle Cell Anaemia in Children in the Gambia: A Cross-Sectional Study. J Hematol Clin Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jhcr.1001033; 9: 001-006
Most Viewed
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic ReviewMohammad Hossein Karami*, Majid Abdouss*, Mandana Karami. Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic Review. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001151; 6: 201-215
-
Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available KnowledgeAvishek Mandal*. Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available Knowledge. Ann Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001039; 7: 001-010
-
Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian RandomizationYong-Qing Zhu, Xiao-Yan Meng, Jing-Hua Yang*. Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001032; 7: 012-022
-
An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergiesNathalie Cottel,Aïcha Dieme,Véronique Orcel,Yannick Chantran,Mélisande Bourgoin-Heck,Jocelyne Just. An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergies. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001027; 5: 030-037

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."